Glucometers and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) are the keys to monitoring glucose. Although both are devices that allow you to monitor your health, glucometer and CGM have some significant differences.
The differences between glucometer and CGM include how they work, focus, accuracy, data provided, and device cost.
This article will explore the key differences between glucometer and CGM for monitoring your glucose.
What is a Glucometer?

A glucometer is an electronic device used in healthcare to measure blood sugar levels. This device allows people with diabetes or anyone who wants to monitor their blood sugar levels to do so regularly and quickly.
With results that are faster than laboratory tests, users can take action more quickly. Users can adjust their diet, exercise, and medication intake if necessary.
What is CGM?

Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a medical device that measures glucose under the skin (interstitial sugar) to help patients stabilize their blood sugar levels.
Most CGMs measure blood sugar levels every few minutes, 24 hours a day. The sensor sends data to a reader, smartphone, or computer that displays blood sugar levels minutes after they are measured.
CGMs help people with diabetes to stay within a target range of blood sugar levels, which is based on age and underlying medical conditions.
The Difference Between Glucometer and CGM
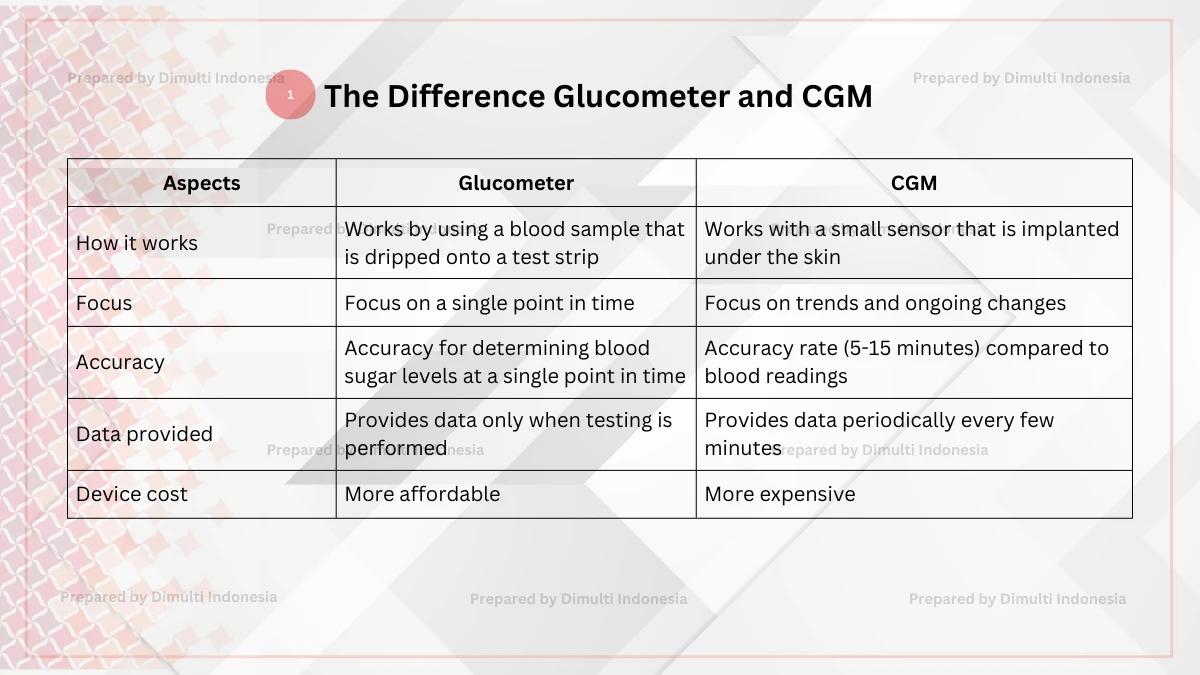
A glucometer and a Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) are devices that allow you to monitor your health. Here are five differences between Glucometer and CGM:
1. How it works
Glucometer: The device works by using a blood sample that is dripped onto a test strip. The device then reads the data and displays the blood sugar level on the screen.
CGM: The device works with a small sensor that is implanted under the skin. The device then continuously measures glucose in the interstitial fluid.
2. Focus
Glucometer: Measurements focus on a single point in time. To track blood sugar trends, regular monitoring is required.
CGM: Measurements focus on trends and ongoing changes. This is suitable for long-term use, as changes can be monitored in real time.
3. Accuracy
Glucometer: Has a high level of accuracy for determining blood sugar levels at a single point in time.
CGM: Has a slightly slower accuracy rate (5-15 minutes) compared to blood readings. However, it provides better monitoring of glucose trends.
4. Data provided
Glucometer: Provides data only when testing is performed. However, those connected to Bluetooth can record each test on a mobile app.
CGM: Provides data periodically every few minutes. Provides an overview of blood sugar level trends.
5. Device cost
Glucometer: One of the advantages of a glucometer is more affordable, but requires ongoing costs for test strips.
CGM: More expensive not only at the initial purchase but also for ongoing costs to replace sensors and transponders.
That’s the difference between glucose and CGM that you can consider when choosing according to your personal needs.
If you need an affordable blood glucose meter for regular measurements, a glucometer is a good choice. However, if you need a blood glucose meter with real-time trend monitoring, you can choose a CGM.