The term "harmonic emission" may be familiar to those who work in telecommunications engineering, electronics, or device testing. But for most other people, this phrase may still sound quite unfamiliar.
Understanding harmonic emission is important, especially in the context of testing information and communications technology (ICT) devices before obtaining official certification from regulators in each country.
For those unfamiliar with harmonic emissions, let's discuss their definition, causes, and importance in the world of ITC devices.
What is Harmonic Emission?

Harmonic emission is an additional frequency signal that appears as a result of a non-linear process in an electronic device or transmitter system. These harmonics are usually multiples of the main frequency (fundamental frequency) being used by the device.
Example of harmonic emission: If a device transmits a main signal at a frequency of 100 MHz, harmonic emissions may appear at 200 MHz (2x), 300 MHz (3x), and so on. Although undesirable, these harmonic signals can still appear due to the natural properties of electronic components such as amplifiers or oscillators.
The Causes of Harmonic Emission
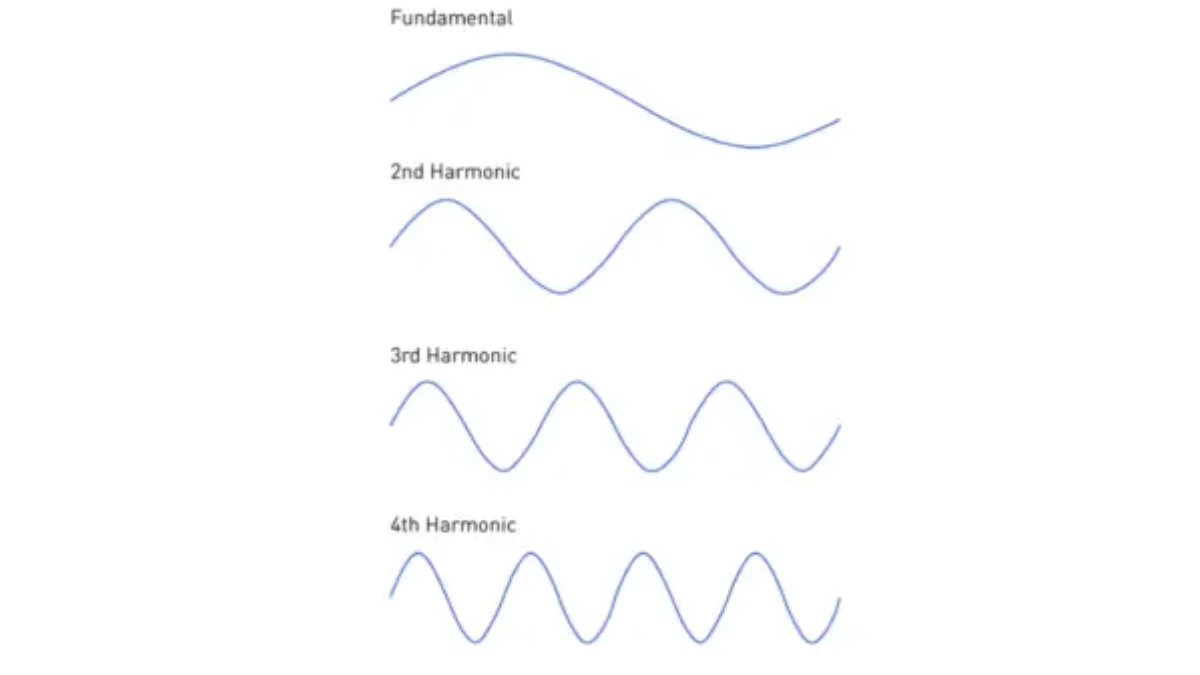
Harmonic emissions can be caused by various factors, depending on the design and quality of the electronic components used. Here are some things that can cause harmonics:
- Nonlinear distortion from active circuits such as transistors
- Filter designs that are not optimal in suppressing additional frequencies
- Poor soldering quality and PCB layout
- Signal overdrive in transmitter circuits
If a device is not designed properly, harmonic signals can be very strong and interfere with other frequencies, including radio, TV, or emergency communications services.
Why Harmonic Emission Must Be Controlled
In the real world, harmonic emission is not just technical “noise.” It can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI) that disrupts other systems in the vicinity. Imagine if communication devices at an airport were disrupted by harmonic emissions from cheap WiFi devices. That would be dangerous, right?
Therefore, many countries set tolerance thresholds for harmonic emissions in the device certification process. The goal is to ensure that devices on the market do not cause interference in the frequency spectrum shared by the public.
Harmonic Emission Standards and Regulations

Each country has its own approach to regulating harmonic emission limits. The goal remains the same, which is to ensure that electronic or telecommunications devices do not interfere with other systems in their vicinity.
Some international standards that are commonly used globally are as follows:
- CISPR 32: For information technology (IT) equipment
- ETSI EN 301 489: For radio devices and communication systems
- IEC 61000-3-2: For harmonic emissions in devices connected to electrical networks (AC power)
That is some information you need to know about harmonic emissions. Although it may sound technical, the impact is real. It can cause interference with important communication services, hinder the certification process, or even lead to product recalls from the market.
If you are developing or importing electronic devices, make sure to always consider harmonic emissions from the initial design stage through to the testing process. Don't fail testing due to a small oversight that could have been prevented from the start by understanding the basic concepts and sources of the problem.