Did you know that there is a small device in your car that quietly collects information every time the vehicle is used? This device is called a telematics box.
Its ability to collect highly important data makes the telematics box assist drivers in operational efficiency, enhance road safety, and even analyze driving behavior.
You may have heard about its capabilities before. But do you understand its functions, how it works, and the regulations surrounding it in Indonesia? This article will help you gain a deeper understanding of the telematics box.
What is a Telematics Box?
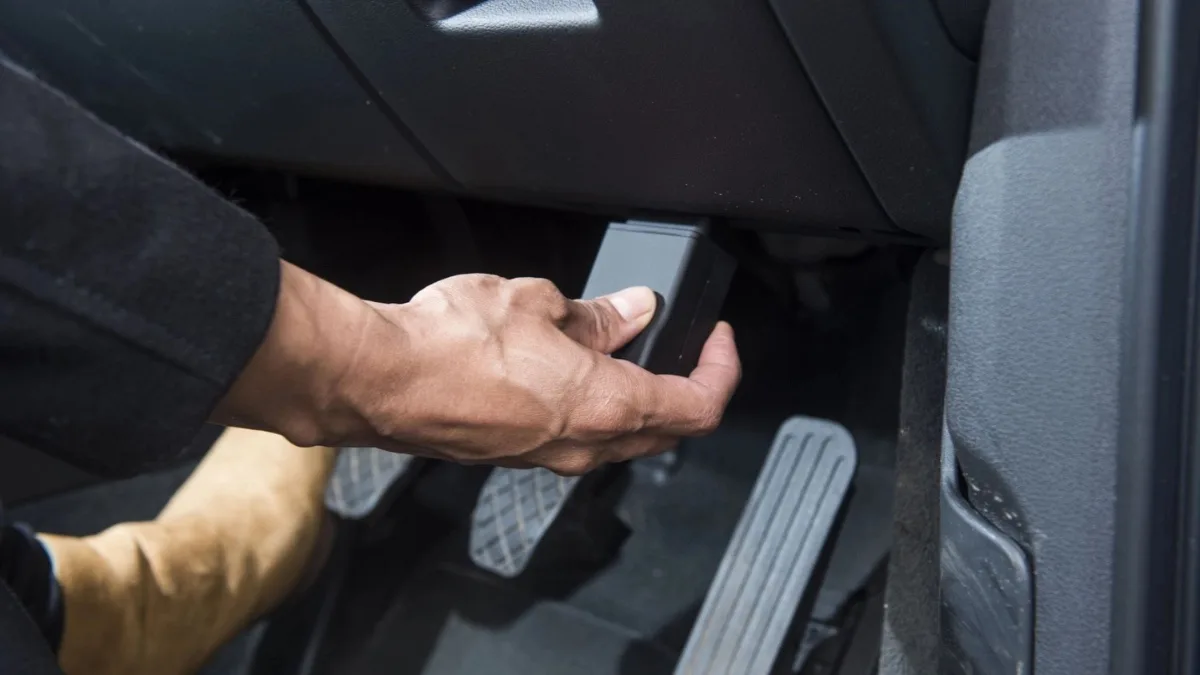

A telematics box is an electronic device installed in a vehicle to monitor its location, collect data on vehicle performance, and driver behavior.
Data on driving speed, braking, acceleration, location, and mileage will be collected by this device for automatic analysis.
The collected data will be sent to a cloud system via a cellular network. This data is useful for providing vehicle owners with accurate insights into vehicle conditions, including fuel consumption, safety, vehicle maintenance, and fleet management.
Since it is installed in a hidden part of the vehicle, this device, also known as a black box, On-Board Unit (OBU), or telematics unit, is often unknown to users.
How Does a Telematics Box Work?
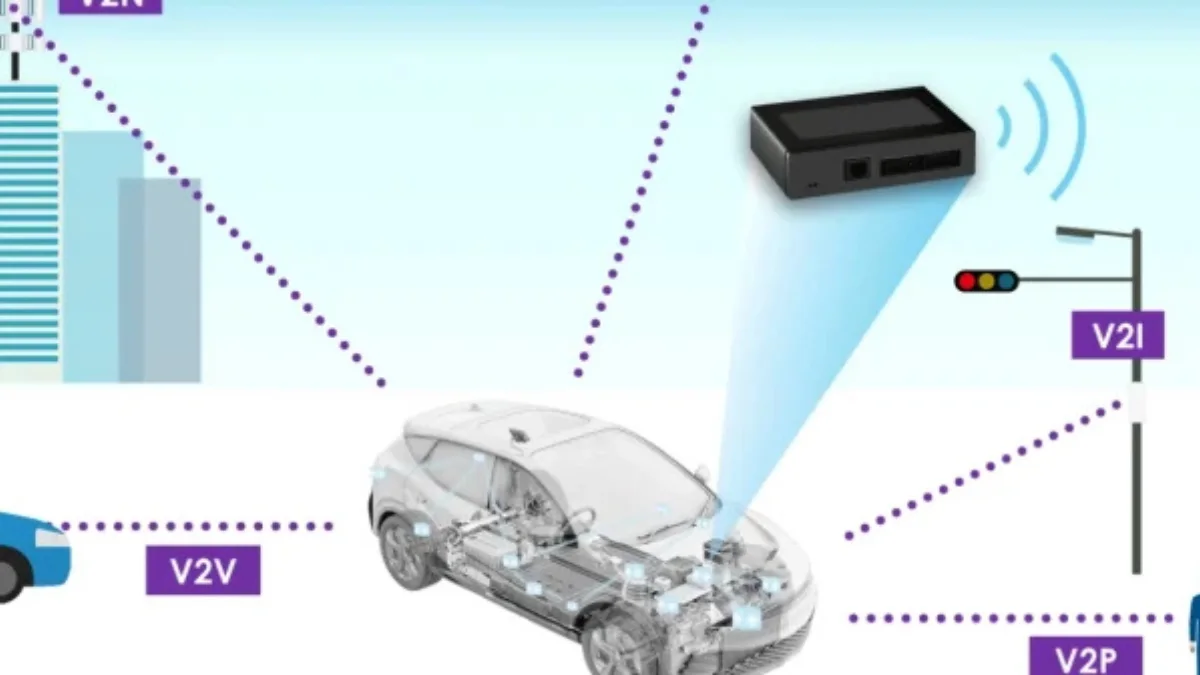
A telematics box works dengan menggabungkan teknologi GPS tracker, sensor kendaraan, dan konektivitas seluler, seperti GSM, WCDMA, atau LTE. Here is how it works in detail:
- Data collection: The device connects to the vehicle's OBD-II port to monitor and record various vehicle data parameters.
- Data transmission: The collected data is then transmitted wirelessly to a telematics server via a cellular network.
- Data analysis: On the server, the data is analyzed to generate information that can be used by relevant parties.
- Information access: The analyzed information can be accessed by users through a secure application or web platform.
Main Component of Telematics Box
- GPS module: Tracks the location of the vehicle in real time.
- Mobile module (GSM, WCDMA, or LTE): Sends data to the server.
- Acceleration and gyroscope sensors: Detect extreme movements occurring on the road.
- OBD-II or CAN bus interface: Component that reads engine data.
- Internal storage: A Component that functions when cellular signals are unavailable.
The Benefits of Telematics Box
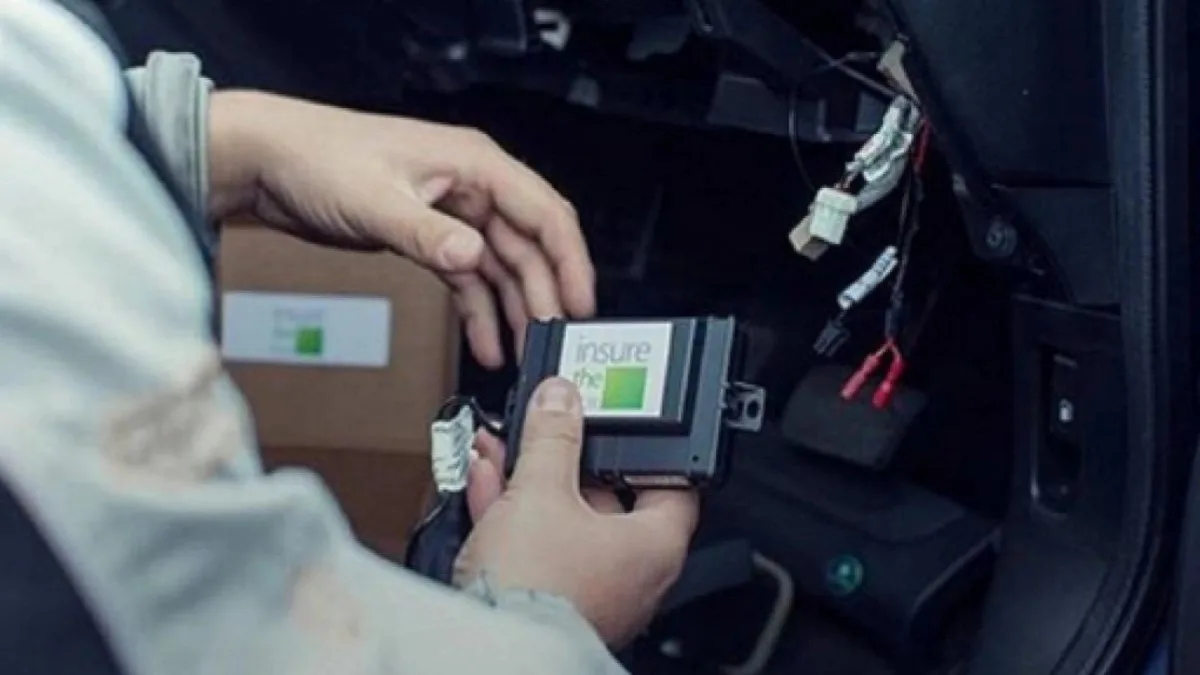

The telematics box provides many benefits, especially in detecting damage early on, tracking vehicle locations, and simplifying insurance claims. Here are some of the main benefits in detail:
1. Detecting damage early on
One of the benefits of a telematics box is that it can detect damage early on. Its ability to read early signs of engine damage allows owners to perform maintenance before the problem gets worse.
2. Driver behavior analysis
Driver behavior analysis is another benefit of this device. For logistics companies, this analysis can be used to find out which drivers often speed or brake suddenly. This data can also be used as a basis for company evaluations and actions regarding drivers.
3. Tracking vehicle locations
Telematics boxes have another benefit in that they can track vehicle locations. This is still useful for logistics companies in knowing the position of their fleet in real time. This capability is certainly very important for ensuring on-time deliveries.
4. Fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is another benefit of this device. Using route data and driving style information, private vehicle owners or logistics companies can develop strategies to prevent vehicles from wasting fuel.
5. Simplifying insurance claims
Another benefit of the telematics box is simplifying insurance claims. Data from this device can serve as strong evidence to support vehicle claims in the event of an accident. For vehicles using this device, some insurance companies can now offer lower premiums.
Telematics Box Regulation in Indonesia

The telematics box uses communication technologies that operate within a specific frequency spectrum.
In Indonesia, a wireless device is required to have a DJID (Directorate General of Digital Infrastructure) under the Ministry of Communication and Digital (KOMDIGI).
Type approval for Telematics box and regulation will be based on the Director General Regulation (PERDIRJEN) No. 5 Tahun 2009, which requires all radio frequency-based devices to meet specific technical standards before being sold in the country.
The DJID certification ensures that the product meets government safety and quality regulations and does not interfere with other communication devices.
The certification process involves technical testing, such as frequency adjustments, safety checks, and compatibility with the surrounding environment.
Once the tests are completed, products that pass are listed in a Test Result Report, which confirms that the product is safe and meets the requirements for sale in Indonesia. This report reassures customers that the product meets technical standards and is secure.
For companies wanting to sell a telematics box in Indonesia, Dimulti as product compliance services are available to assist with this process.
This service includes preparing technical and legal documents, conducting required testing, ensuring compliance with regulations, helping companies streamline the certification process, and giving consumers confidence in certified products. [UN]