A pacemaker is a medical device implanted in the body, usually in the chest, to help regulate the heart rhythm. There are many types of pacemakers with different service lives and installation.
Each patient's medical needs will determine the type of pacemaker used. This article will discuss the types of pacemakers that are commonly used. Let's take a look so you don't make the wrong choice for your needs.
Types of Pacemakers

In general, pacemakers are divided into several types based on their lifespan and installation, the number of heart chambers stimulated, and their technology. Each type has different advantages. Here is a more detailed explanation.
Based on lifespan and installation
Permanent pacemaker
A permanent pacemaker is implanted under the skin in the chest. This device is installed through minor surgery to place the implanted pulse generator. The cable is then inserted into the blood vessel until it reaches the heart.
Problems with the heart's electrical system that do not function properly can be overcome by a pacemaker to normalize its rhythm. This device is suitable for long-term use, often for life. Suitable for patients with chronic heart rhythm disorders.
Temporary pacemaker
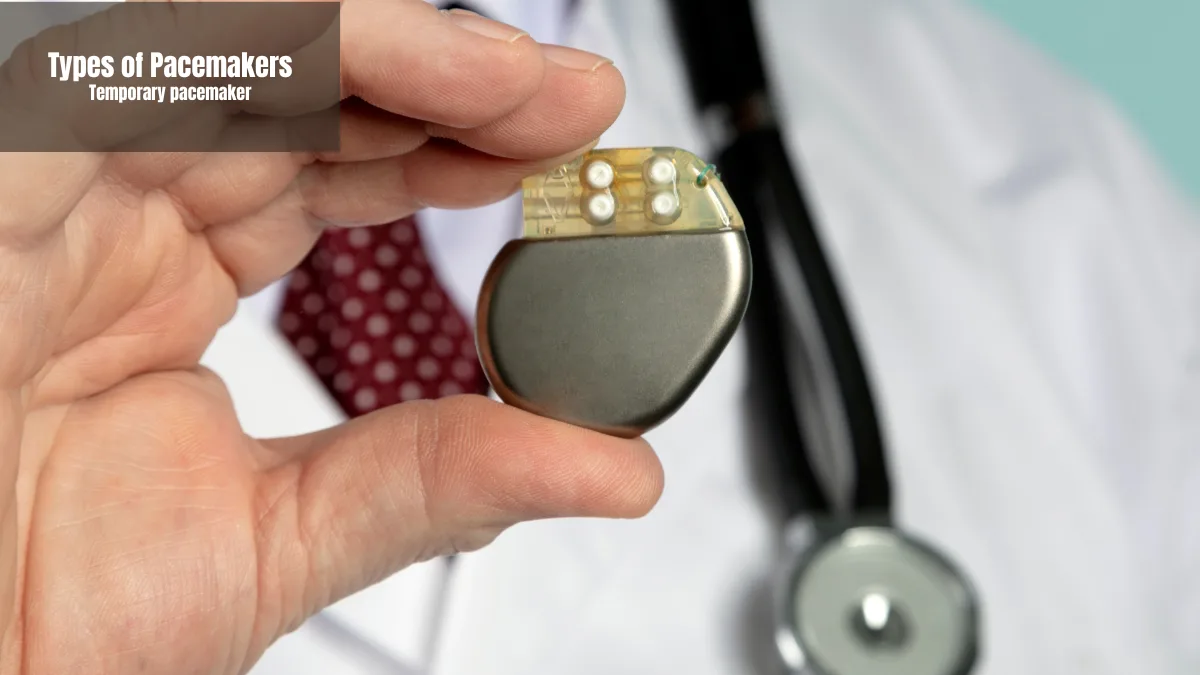
A temporary pacemaker is a type that is not permanently implanted under the skin. Although some are implanted temporarily, they are usually placed outside the body and connected with temporary wires.
In emergencies or during recovery after heart surgery, this device is used to restore the heart rhythm. In addition, the heart rate will be kept normal for a certain period of time, ranging from days to weeks, until the patient's condition stabilizes.
Based on the number of heart chambers stimulated
Single-chamber pacemaker
A single-chamber pacemaker is a type that uses only one cable to stimulate one heart chamber, usually the right ventricle. Its purpose is to ensure that the heart beats at the correct rhythm.
Patients with less complex heart rhythm disorders, such as bradycardia or heart block, are suitable candidates for this device.
Dual-chamber pacemaker
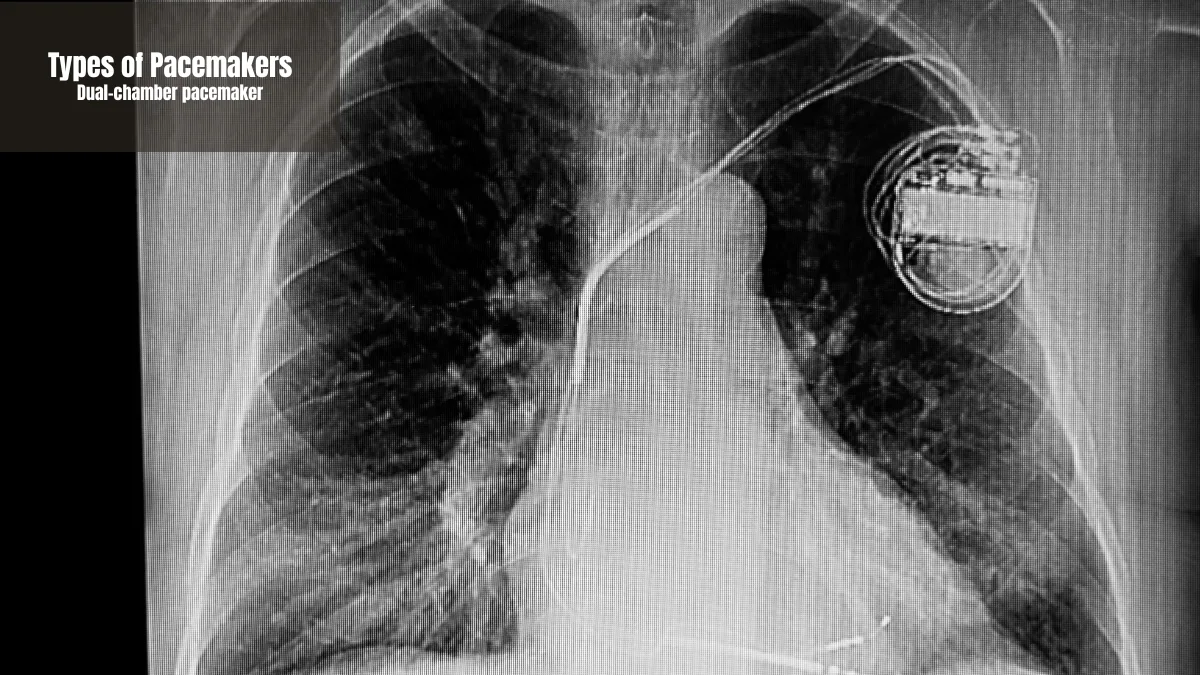
A dual-chamber pacemaker is a type that uses two wires to stimulate the right atrium and right ventricle. The goal is to synchronize blood pumping in both chambers of the heart at the same time.
Heart rhythm problems that require better coordination between the heart chambers are best treated with this device. This device will reduce symptoms of dizziness or fatigue due to more efficient blood flow.
Biventricular pacemaker
A biventricular pacemaker is a type that uses three wires to stimulate the right and left ventricles. The goal is to make both sides of the heart pump blood more synchronously.
Severe heart failure and heart rhythm disorders can be helped with this device. The patient's quality of life will improve with this therapy that enhances heart performance.
Based on technology
Leadless pacemaker
Leadless pacemakers are the latest type of pacemaker, which are much smaller in size. The device is implanted directly into the heart chamber through a blood vessel without electrode wires.
The risk of complications from using this device is very low. The implantation procedure is also simpler and does not leave a pocket under the skin. However, its use requires strict medical consideration because not all patients are suitable for a leadless pacemaker.
These are the types of pacemakers that you need to know to have the best for your needs. By understanding the different types, you can make an informed decision before purchasing one.
Each type of pacemaker has its own advantages and disadvantages. Depending on the patient's condition, the device may be permanently implanted or not.
Based on the number of chambers and stimulation, there are three types: single-chamber pacemakers for less complex disorders, dual-chamber pacemakers for synchronizing both chambers of the heart, and biventricular pacemakers to improve the patient's life with therapy.
The most recent development is the leadless pacemaker, which has the lowest risk but requires strict medical consideration. With the right pacemaker, your heart will beat at a stable rhythm and your health will be maintained. [UN]