Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) and fiber optic are the keys to providing internet access. Although both improve the connection, VSAT vs fiber optic have some significant differences.
The differences between VSAT vs fiber optic include technology, range, speed, infrastructure, necessity, and stability.
This article will explore the key differences between VSAT vs fiber optic to enhance the connection for the internet.
What is a VSAT?

A Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) is a communication system that utilizes a small satellite dish to establish a connection with satellites. This device has a small antenna measuring only about 1 to 3 meters.
However, don't let its size fool you—this compact device can transmit signals to hard-to-reach areas. It is used in remote villages to access the internet. To function, VSAT does not require tall towers or long cables; it only needs an open sky.
What is a Fiber Optic?

Fiber optics is a cable technology that transmits data in the form of light signals through very thin glass or plastic fibers. These cables enable high-speed, high-capacity, long-distance data transmission.
Fiber optics can convert electrical signals into light waves and transmit them through the fibers by utilizing the principles of light reflection and refraction. This cable system is resistant to electromagnetic interference. This is certainly very necessary for internet communication networks.
The Differences Between VSAT vs Fiber Optic
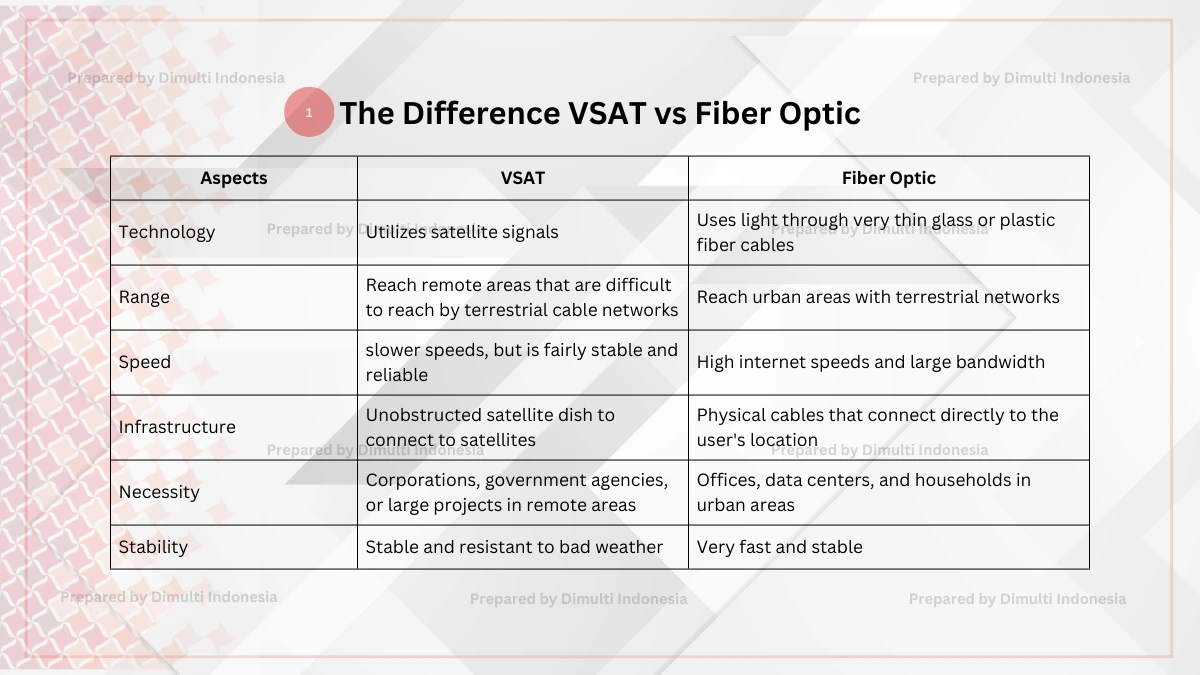
A VSAT and a fiber optic link are both key to providing internet access. Here are six differences between VSAT vs fiber optic:
1. Technology
VSAT: Uses technology that utilizes satellite signals as the main connecting medium.
Fiber optic: Uses light through very thin glass or plastic fiber cables to transmit data.
2. Range
VSAT: Able to reach remote areas, rural areas, or locations that are difficult to reach by terrestrial cable networks.
Fiber optic: Typically reaches urban areas with terrestrial networks on existing cable infrastructure.
3. Speed
VSAT: Has slower speeds than fiber optic, but is fairly stable and reliable.
Fiber optic: Has high internet speeds and a large bandwidth with low latency.
4. Infrastructure
VSAT: Uses a small, unobstructed satellite dish to connect to satellites in the sky.
Fiber optic: Uses physical cables that connect directly to the user's location. Requires complex and time-consuming installation in areas that are not yet covered.
5. Necessity
VSAT: Suitable for use by corporations, government agencies, or large projects in remote areas.
Fiber optic: Suitable for offices, data centers, and households in urban areas that need wide bandwidth.
6. Stability
VSAT: Known for being stable and resistant to bad weather. Not dependent on signal conditions on the ground.
Fiber optic: Known for being very fast and stable because it does not use electrical signals or radio waves.
That’s the difference between VSAT vs Starlink that you can consider when choosing according to your personal needs.
If you are looking for internet for remote areas, a VSAT is a good choice. However, if you need the internet in an urban area, you can choose a fiber optic connection.