A WiFi extender and an access point are the keys to extending the WiFi range. Although both maximize the expansion of internet connection, WiFi extender vs access point have some significant differences.
The differences between WiFi extender vs access point include functions, how it works, performance, network requirements, and usage requirements.
This article will delve into the important differences between WiFi extender vs access point for extending the WiFi range.
What is a WiFi Extender?

A WiFi extender is an electronic device used to extend the range of a WiFi signal to a new network. This device receives signals from the main router via a connected Ethernet cable to amplify the signal and broadcast it to a wider area.
By creating a new network, the WiFi extender does not reduce the bandwidth of the main router. This means that the signal strength remains the same before and after installing this device.
What is an Access Point?

An access point is a device that allows various devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, to connect to the internet wirelessly (via WiFi).
This tool acts as a liaison between wired networks and wireless devices so that the internet connection can reach a wider area and remain stable.
Technically, the access point transmits WiFi signals with the help of antennas and transceivers.
Generally, these devices are connected to a router, switch, or hub using an Ethernet cable to expand network coverage.
The Difference Between WiFi Extender vs Access Point
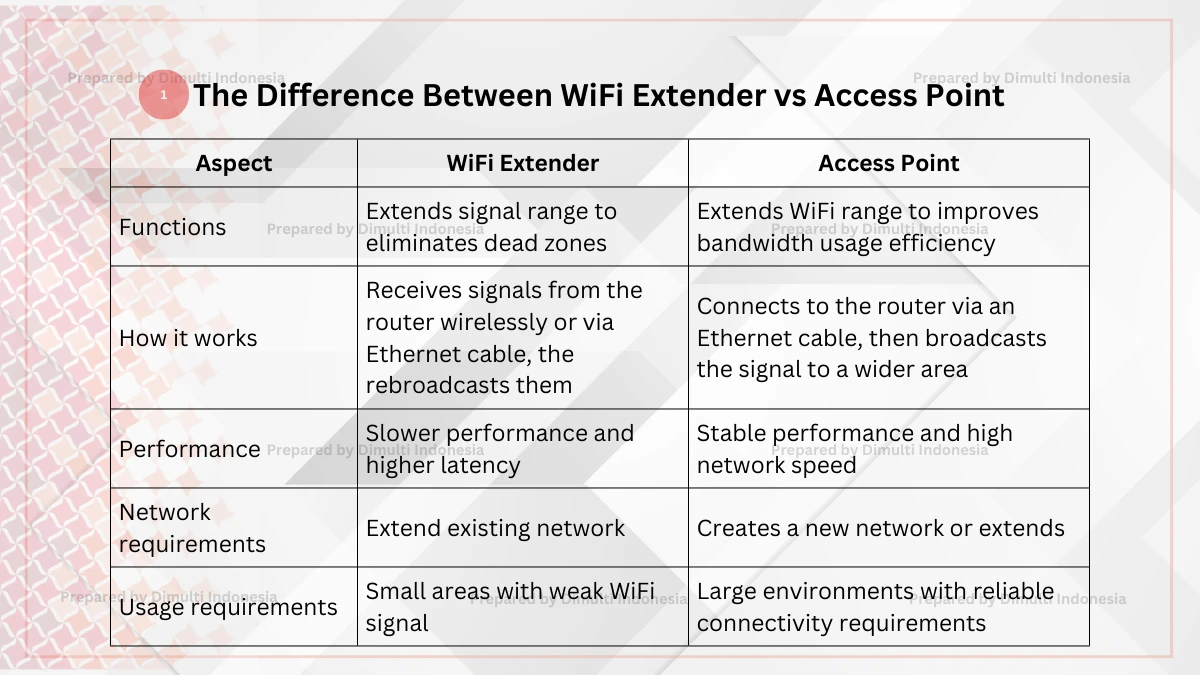
A WiFi extender and an access point are both used to extend the WiFi range, but they have some differences. Here are five differences between WiFi extender vs access point:
1. Functions
WiFi extender: Extends signal range, creates a more stable connection, and eliminates dead zones.
Access point: Extends WiFi range, supports multiple device connections, and improves bandwidth usage efficiency.
2. How it works
WiFi extender: Receives signals from the router, amplifies them, and rebroadcasts them using the same SSID as the router. Some can be connected to the router via an Ethernet cable.
Access point: Connects to the router via an Ethernet cable, then broadcasts the signal to a wider area, and can have a different SSID from the main router.
3. Performance
WiFi extender: Compared to an access point, an extender has slower performance and higher latency.
Access point: Offers more stable performance and high network speed.
4. Network requirements
WiFi extender: Extends the range of an existing network from the main router.
Access point: Creates a new network or extends an existing network.
5. Usage requirements
WiFi extender: Suitable for use in small areas with weak WiFi coverage.
Access point: Can be used in large environments with reliable connectivity requirements.
That’s the difference between WiFi extender vs access point that you can consider when choosing according to your personal needs.
If you need a suitable use in small areas with weak or no WiFi signal, a WiFi extender is a good choice. However, if you need to ensure stable internet connectivity in areas with many users, you can choose a WiFi mesh. [UN]