Flowmeters are the key to measuring fluid flow in piping systems or open channels. Although all types of devices allow you to control flow, there are some significant differences between electromagnetic and turbine flowmeters.
The differences between electromagnetic and turbine flowmeters include work principle, types of fluids that can be measured, installation, advantages, and application examples.
This article will explore the key differences between electromagnetic and turbine flowmeters to control flow in several industries.
What is an Electromagnetic Flowmeter?
An electromagnetic flowmeter is a type of device used to measure the flow rate of conductive liquids such as water, liquid waste, and chemical solutions. These devices use the principle of electromagnetic induction to determine the speed of flowing liquids. The readings of these devices are not affected by pressure, temperature, or viscosity, resulting in accurate data.
Various industries, such as water treatment, manufacturing, energy, and food processing, use these devices because of their high-precision measurement capabilities and minimal maintenance requirements. Some modern models are equipped with Bluetooth connectivity so they can be operated remotely via a smartphone or computer.
What is a Turbine Flowmeter?
A turbine flowmeter is a type of flowmeter that measures the flow rate of liquids or gases using the principle of turbine rotation inside a pipe. It works by measuring the flow rate or volume through the speed of the turbine rotation when the fluid flows.
The advantages of this type of flowmeter are high accuracy, easy installation and maintenance, simple design, durability, and fast response. In addition, it has a wide flow range and is capable of operating at various temperatures and pressures.
Sectors that use this flowmeter include the oil and gas, water and wastewater, and food and beverage industries. This device is even commonly used in the chemical industry and the agricultural sector.
The Differences of Electromagnetic and Turbine Flowmeters
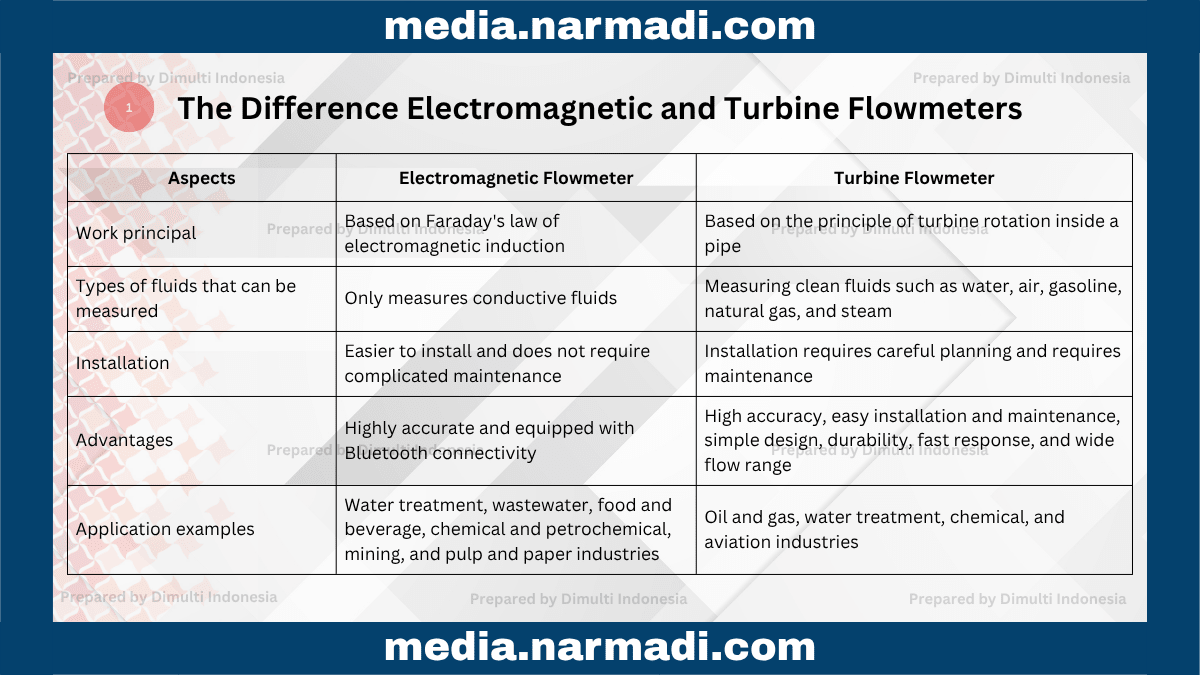
Electromagnetic and turbine flowmeters are devices that allow you to have good safety. Here are the differences between them:
Work principle
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Operates based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which measures the voltage induced when a conductive fluid cuts through a magnetic field.
Turbine flowmeter: Operates based on the principle of turbine rotation inside a pipe, which measures the flow rate or volume through the speed of the turbine rotation when the fluid flows.
Types of fluids that can be measured
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Only measures conductive fluids, such as water, wastewater, and most chemicals.
Turbine flowmeter: Measuring clean fluids such as water, air, gasoline, natural gas, and steam.
Installation
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Easier to install and does not require complicated maintenance.
Turbine flowmeter: Installation requires careful planning and requires maintenance and periodic calibration to ensure accuracy.
Advantages
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Highly accurate and equipped with Bluetooth connectivity for remote control.
Turbine flowmeter: High accuracy, easy installation and maintenance, simple design, durability, fast response, and wide flow range.
Application examples
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Used in water treatment, wastewater, food and beverage, chemical and petrochemical, mining, and pulp and paper industries.
Turbine flowmeter: Used in the oil and gas, water treatment, chemical, and aviation industries.
That’s the difference between electromagnetic vs turbine flowmeters that you can consider when choosing according to your personal needs.
If you want a liquid meter with high accuracy and Bluetooth connectivity for remote control, an electromagnetic flowmeter is a good choice. However, if you want a simple design, durability, fast response, and a wide flow range, you can choose a turbine flowmeter.